The significant increase in air pollution is driven by various factors, including industrialization, urbanization, deforestation, agricultural practices, climate change, and population growth, resulting in severe consequences for both the environment and human health. This upsurge in pollutants, primarily attributable to the combustion of fossil fuels and other human activities, has led to a rise in respiratory and cardiovascular diseases, environmental degradation, economic burdens, and a reduced quality of life in affected regions. To tackle this escalating crisis, it is essential that governments, industries, and communities worldwide prioritize the transition to clean energy, enforce stricter regulations, promote sustainable practices, raise public awareness, and engage in international cooperation to mitigate the global impact of air pollution. We Have Researched and Find Out The Top Ten Most Polluted Cities in the World.
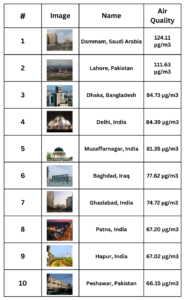
Top Ten Most Polluted Cities in the World in 2023
10. Peshawar, Pakistan (66.15 µg/m3)
Peshawar, Pakistan, faces a serious air pollution problem. Rapid urbanization, industrial growth, and increased vehicular traffic have led to high levels of pollution, particularly from older vehicles and industries. This pollution is causing health issues among residents, including respiratory and cardiovascular problems. To tackle this issue, Peshawar needs to transition to cleaner energy sources, enforce stricter emissions standards, and raise public awareness about the importance of air quality for both health and the environment.
9. Hapur, India (67.02 µg/m3)
Hapur, a city in Uttar Pradesh, India, is facing significant air pollution issues primarily due to industrial emissions, traffic, construction activities, and agricultural practices. This pollution, characterized by high levels of particulate matter and harmful gases, poses health risks to residents, leading to respiratory problems and allergies. Addressing Hapur’s air pollution problem requires stricter emissions control, promoting cleaner transportation, sustainable urban planning, and raising public awareness about air quality and its health impacts.
8. Patna, India (67.20 µg/m3)
Patna, the capital city of Bihar in India, is grappling with a severe air pollution problem. The city’s air quality is adversely affected by factors such as industrial emissions, heavy traffic, construction activities, and agricultural practices. These activities release a significant amount of pollutants into the air, leading to elevated levels of particulate matter and harmful gases. Patna’s residents face health risks, including respiratory issues and allergies, due to this pollution. To combat the air pollution crisis in Patna, it is imperative to implement stringent emissions controls, promote cleaner modes of transportation, adopt sustainable urban planning practices, and enhance public awareness regarding air quality and its health implications.
7. Ghaziabad, India (74.72 µg/m3)
Ghaziabad, a city in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh, is confronted with a severe air pollution problem. The city’s air quality is heavily impacted by a combination of factors, including industrial emissions, vehicular congestion, construction activities, and agricultural practices. These activities contribute to high levels of particulate matter and harmful gases in the atmosphere. Ghaziabad’s residents are exposed to health risks such as respiratory ailments and allergies due to this pollution. To address the air pollution crisis in Ghaziabad, it is essential to implement stringent emissions controls, promote cleaner transportation options, adopt sustainable urban planning strategies, and increase public awareness about air quality and its associated health hazards.
6. Baghdad, Iraq (77.62 µg/m3)
Baghdad, the capital city of Iraq, faces a significant air pollution challenge. The city’s air quality is impacted by multiple factors, including industrial emissions, vehicular traffic, power generation, and dust storms, which are common in the region. These factors contribute to high levels of particulate matter (PM2.5) and other pollutants in the atmosphere. As a result, Baghdad’s residents are at risk of health problems such as respiratory issues and cardiovascular diseases. To address air pollution in Baghdad, there is a need for improved emissions controls, the promotion of cleaner transportation options, urban planning that considers environmental factors, and public awareness campaigns to educate residents about the importance of air quality and its impact on health and well-being.
5. Muzaffarnagar, India (81.35 µg/m3)
Muzaffarnagar, a city in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh, also faces air pollution challenges. The city’s air quality is influenced by various factors, including industrial emissions, vehicular traffic, agricultural activities, and urban development. These factors contribute to elevated levels of particulate matter (PM2.5) and harmful gases in the air. Residents of Muzaffarnagar are at risk of health issues, including respiratory problems and allergies, due to this pollution. Addressing air pollution in Muzaffarnagar requires implementing stricter emissions controls, promoting cleaner modes of transportation, adopting sustainable urban planning practices, and raising public awareness about air quality and its health impacts.
4. Delhi, India (84.39 µg/m3)
Delhi, the capital of India, has gained notoriety for its severe air pollution problem. The city’s air quality is affected by a complex interplay of factors, including industrial emissions, vehicular congestion, construction activities, agricultural residue burning, and weather conditions that trap pollutants. These factors lead to consistently high levels of particulate matter (PM2.5) and noxious gases in the atmosphere, resulting in a public health crisis. Residents of Delhi face a range of health issues, including respiratory diseases, cardiovascular problems, and a decreased quality of life. To combat air pollution in Delhi, comprehensive measures are needed, including stricter emissions standards, promotion of cleaner transportation options, waste management improvements, green initiatives, and extensive public awareness campaigns about the importance of air quality and its impact on health and the environment.
3. Dhaka, Bangladesh (84.73 µg/m3)
In Dhaka, rapid urbanization, industrial emissions, and vehicular congestion contribute to poor air quality. The city experiences high levels of particulate matter (PM2.5) and other pollutants, leading to respiratory problems and reduced quality of life for its residents. Addressing air pollution in Dhaka requires better urban planning, stricter emissions controls, and public awareness campaigns.
2. Lahore, Pakistan (111.63 µg/m3)
Lahore, Pakistan, faces similar challenges with industrial emissions, agricultural residue burning, and vehicular pollution being major contributors to air pollution. Lahore often experiences hazardous levels of smog, particularly during the winter months. Mitigating air pollution in Lahore necessitates implementing cleaner transportation options, reducing crop burning, and enforcing emissions standards.
1. Dammam, Saudi Arabia (124.11 µg/m3)
Dammam, located in the Eastern Province of Saudi Arabia, is affected by industrial emissions and desert dust storms. Air quality in Dammam can vary due to factors like weather conditions and industrial activity. Measures to improve air quality in Dammam include emissions control in industries, dust suppression techniques, and monitoring air quality during dust storms.
Table Form : Top Ten Most Polluted Cities in the World in 2023