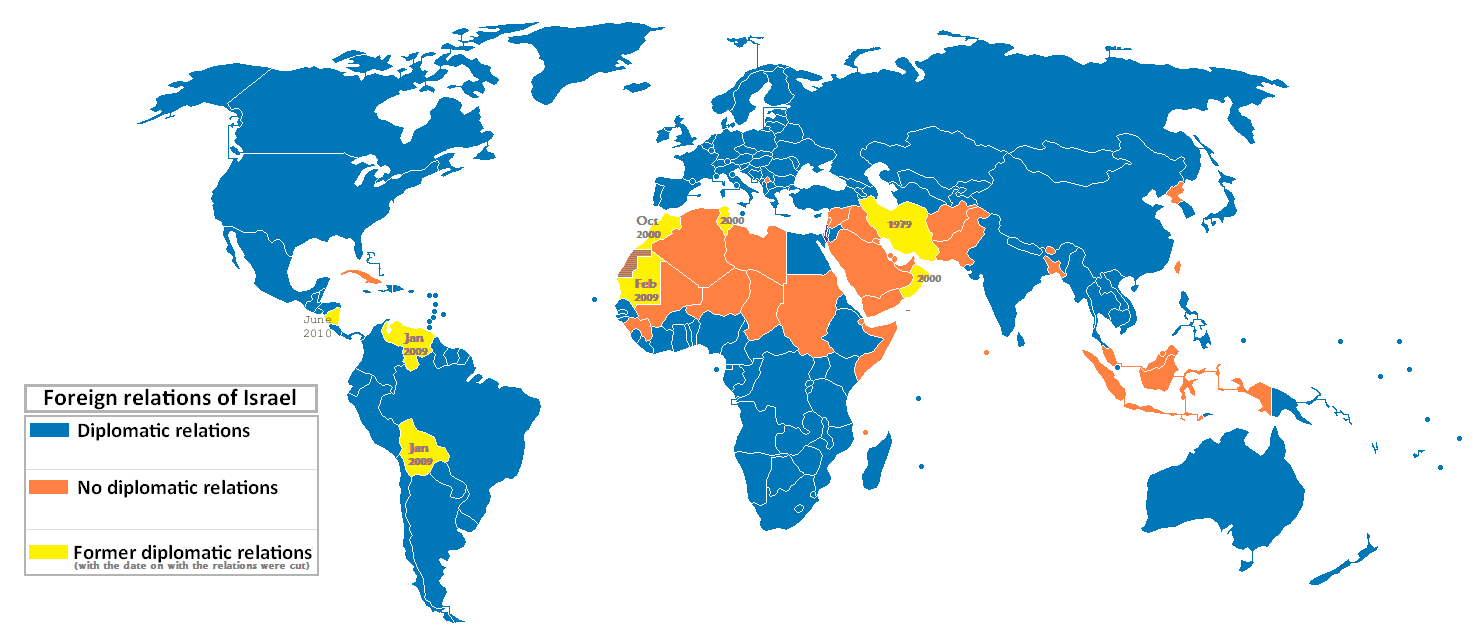
Israel’s foreign relations have been a dynamic and complex aspect of its existence since its establishment in 1948. Situated in a region characterized by political instability and ongoing conflicts, Israel has strategically cultivated diplomatic ties with countries around the world to ensure its security and promote its interests. Let’s see Israel Relations with the help of Table Data below.
Israel Relations with every Country
| Countries | Relations | |
| 1 | Uganda | Yes |
| 2 | Uzbekistan | Yes |
| 3 | Austria | Yes |
| 4 | Australia | Yes |
| 5 | Ukraine | Yes |
| 6 | Uruguay | Yes |
| 7 | Azerbaijan | Yes |
| 8 | The United Arab Emirates | Yes |
| 9 | Italy | Yes |
| 10 | Bahamas | Yes |
| 11 | Marshall Islands | Yes |
| 12 | Seychelles | Yes |
| 13 | Cook Islands | Yes |
| 14 | Solomon Islands | Yes |
| 15 | Indonesia | No |
| 16 | Iceland | Yes |
| 17 | Ireland | Yes |
| 18 | Iran | No |
| 19 | El Salvador | Yes |
| 20 | Albania | Yes |
| 21 | Algeria | No |
| 22 | Angola | Yes |
| 23 | Andorra | Yes |
| 24 | Antigua & Barbuda | Yes |
| 25 | Eswatini | Yes |
| 26 | Estonia | Yes |
| 27 | Afghanistan | No |
| 28 | Ecuador | Yes |
| 29 | Argentina | Yes |
| 30 | Eritrea | Yes |
| 31 | Armenia | Yes |
| 32 | United States | Yes |
| 33 | Ethiopia | Yes |
| 34 | The Kingdom of Bhutan | Yes |
| 35 | Bulgaria | Yes |
| 36 | Bolivia | Yes |
| 37 | Bosnia and Herzegovina | Yes |
| 38 | Burundi | Yes |
| 39 | Botswana | Yes |
| 40 | Burkina Faso | Yes |
| 41 | Bahrain | Yes |
| 42 | Belarus | Yes |
| 43 | Belgium | Yes |
| 44 | Belize | Yes |
| 45 | Bangladesh | No |
| 46 | Benin | Yes |
| 47 | Barbados | Yes |
| 48 | Brunei | No |
| 49 | Brazil | Yes |
| 50 | United Kingdom | Yes |
| 51 | Gabon | Yes |
| 52 | Ghana | Yes |
| 53 | Guatemala | Yes |
| 54 | Guyana | Yes |
| 55 | Georgia | Yes |
| 56 | Djibouti | No |
| 57 | Guinea | Yes |
| 58 | Guinea-Bissau | Yes |
| 59 | Equatorial Guinea | Yes |
| 60 | Jamaica | Yes |
| 61 | Gambia | Yes |
| 62 | Germany | Yes |
| 63 | Grenada | Yes |
| 64 | Dominica | Yes |
| 65 | Denmark | Yes |
| 66 | South Africa | Yes |
| 67 | S. Sudan | Yes |
| 68 | Haiti | Yes |
| 69 | Maldives | No |
| 70 | India | Yes |
| 71 | Netherlands | Yes |
| 72 | Hungary | Yes |
| 73 | Honduras | Yes |
| 74 | Dominican Republic | Yes |
| 75 | Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) | Yes |
| 76 | Holy See (Vatican) | Yes |
| 77 | Vietnam | Yes |
| 78 | Vanuatu | Yes |
| 79 | Venezuela | No |
| 80 | Zimbabwe | Yes |
| 81 | Zambia | Yes |
| 82 | Côte d’Ivoire | Yes |
| 83 | Tajikistan | Yes |
| 84 | Tuvalu | Yes |
| 85 | Togo | Yes |
| 86 | Tonga | Yes |
| 87 | Tanzania | Yes |
| 88 | Trinidad and Tobago | Yes |
| 89 | Greece | Yes |
| 90 | Japan | Yes |
| 91 | Jordan | Yes |
| 92 | Kuwait | No |
| 93 | Lao PDR | Yes |
| 94 | Lebanon | No |
| 95 | Libya | No |
| 96 | Luxembourg | Yes |
| 97 | Latvia | Yes |
| 98 | Liberia | Yes |
| 99 | Lithuania | Yes |
| 100 | Liechtenstein | Yes |
| 101 | Lesotho | Yes |
| 102 | Mauritania | No |
| 103 | Mauritius | Yes |
| 104 | Mali | No |
| 105 | Madagascar | Yes |
| 106 | Mozambique | Yes |
| 107 | Moldova | Yes |
| 108 | Mongolia | Yes |
| 109 | Montenegro | Yes |
| 110 | Monaco | Yes |
| 111 | East Timor | Yes |
| 112 | Myanmar | Yes |
| 113 | Micronesia, Fed. St. | Yes |
| 114 | Malawi | Yes |
| 115 | Malaysia | No |
| 116 | Malta | Yes |
| 117 | Egypt | Yes |
| 118 | Mexico | Yes |
| 119 | Morocco | Yes |
| 120 | Nauru | Yes |
| 121 | Norway | Yes |
| 122 | Niger | No |
| 123 | Nigeria | Yes |
| 124 | New Zealand | Yes |
| 125 | Nicaragua | Yes |
| 126 | Namibia | Yes |
| 127 | Nepal | Yes |
| 128 | Sao Tome & Principe | Yes |
| 129 | Sudan | No |
| 130 | Somalia | No |
| 131 | Syria | No |
| 132 | Suriname | Yes |
| 133 | Sierra Leone | Yes |
| 134 | China | Yes |
| 135 | Singapore | Yes |
| 136 | Slovenia | Yes |
| 137 | Slovakia | Yes |
| 138 | Samoa | Yes |
| 139 | San Marino | Yes |
| 140 | Senegal | Yes |
| 141 | Saint Vincent and the Grenadines | Yes |
| 142 | Saint Lucia | Yes |
| 143 | Saint Kitts & Nevis | Yes |
| 144 | Spain | Yes |
| 145 | Saudi Arabia | No |
| 146 | Serbia | Yes |
| 147 | Sri Lanka | Yes |
| 148 | Oman | No |
| 149 | Iraq | No |
| 150 | Poland | Yes |
| 151 | Portugal | Yes |
| 152 | Fiji | Yes |
| 153 | Philippines | Yes |
| 154 | Finland | Yes |
| 155 | Palau | Yes |
| 156 | Panama | Yes |
| 157 | Papua New Guinea | Yes |
| 158 | Pakistan | No |
| 159 | Paraguay | Yes |
| 160 | Peru | Yes |
| 161 | Chad | Yes |
| 162 | Chile | Yes |
| 163 | Czech Republic | Yes |
| 164 | North Macedonia | Yes |
| 165 | North Korea (DPRK) | No |
| 166 | France | Yes |
| 167 | Colombia | Yes |
| 168 | Cuba | No |
| 169 | Comoros | No |
| 170 | Congo | Yes |
| 171 | Kosovo | Yes |
| 172 | Costa Rica | Yes |
| 173 | Republic of Korea | Yes |
| 174 | Kazakhstan | Yes |
| 175 | Qatar | No |
| 176 | Cape Verde | Yes |
| 177 | Kyrgyzstan | Yes |
| 178 | Kiribati | Yes |
| 179 | Cambodia | Yes |
| 180 | Cameroon | Yes |
| 181 | Canada | Yes |
| 182 | Kenya | Yes |
| 183 | Cyprus | Yes |
| 184 | Croatia | Yes |
| 185 | Rwanda | Yes |
| 186 | Romania | Yes |
| 187 | Russia | Yes |
| 188 | Central African Republic | Yes |
| 189 | Sweden | Yes |
| 190 | Switzerland | Yes |
| 191 | Thailand | Yes |
| 192 | Tunisia | No |
| 193 | Turkey | Yes |
| 194 | Turkmenistan | Yes |
| 195 | Yemen | No |
What is Israel vs Hamas Conflict (Full Story)
The Israel-Hamas conflict is a long and complicated problem tied to the larger issue of Israel and Palestine. It involves Israel, a country created in 1948, and Hamas, a Palestinian group formed in 1987. The conflict is mainly about land, who governs it, and safety concerns.
Historical Background:
This conflict started a long time ago when Jewish people began moving to Palestine to create a Jewish homeland. This caused tension with the Arab people who were already living there.
Formation of Israel and Palestinian Displacement:
In 1947, the United Nations decided to split Palestine into separate Jewish and Arab parts. Israel became a country in 1948, and this led to a war with nearby Arab countries. Many Palestinians were forced to leave their homes and became refugees in neighboring countries.
Rise of Hamas:
Hamas came about in 1987 during a Palestinian uprising against Israeli occupation. It was formed to resist what it saw as Israeli oppression.
Conflict Escalations:
The Israel-Hamas conflict has seen many big fights, like in 2008-2009, 2012, and 2014. These wars caused a lot of damage and suffering in the Gaza Strip, a place controlled by Hamas. The main issues include rockets fired from Gaza into Israel, Israeli airstrikes in response, and a blockade on Gaza that stops goods and people from moving freely.
Key Issues:
1. Territorial Disputes: The main problem is who gets to control the land, including East Jerusalem, the West Bank, and Gaza. Palestinians want their own country in these areas, while Israel insists on its right to exist and have secure borders.
2. Security Concerns: Israel worries about its safety because of rocket attacks from Gaza. Hamas says it uses these attacks to resist what it sees as Israeli mistreatment.
3. Humanitarian Impact: The conflict has hurt many people, especially in Gaza, where there’s been lots of violence. People there also struggle because of a lack of goods and tough living conditions due to the blockade.
4. Political and Religious Dimensions: Religion and politics are big parts of this problem. Both sides claim a deep connection to the land, especially Jerusalem.
International Involvement:
Many countries and groups have tried to solve this conflict, with peace talks and agreements to stop fighting. But it’s been hard to find a lasting solution because of the deep-rooted issues involved.
In short, the Israel-Hamas conflict is a complicated and long-lasting problem that has caused a lot of suffering for both sides. Finding a way to bring peace between Israelis and Palestinians is still a big challenge for everyone involved.
Israel and Hamas Conflict 2023 (October)
On October 7, 2023, Hamas launched a significant offensive against Israel, originating from the Gaza Strip. This offensive involved breaching the Gaza-Israel barrier and gaining entry into Gaza border crossings, nearby Israeli cities, military installations, and civilian settlements. It marks the first direct conflict within Israel’s recognized territory since the 1948 Arab-Israeli War.
The hostilities began early in the morning with a barrage of rockets fired into Israel. Simultaneously, vehicle-transported incursions were made into Israeli territory, resulting in several attacks on neighboring Israeli civilian communities and military bases. Some observers have characterized these events as the onset of a potential third Palestinian intifada.